Basic Concept of Shaft Alignment and how to set it
What is Shaft Alignment
Shaft alignment, or shaft centering, is a crucial process in maintaining the balance and efficient operation of machinery. The following are important principles to consider before performing shaft alignment: Today, we will explain various factors involved in shaft alignment, such as soft foot, shim plates, spacer shafts, and cardan shafts. Additionally, we will introduce tools and methods for correction.
Shaft alignment
Shaft alignment is a critical process in maintaining the balance and efficiency of machinery across various industries such as manufacturing, processing, energy, and automotive. Proper shaft alignment is extremely important as it impacts safety, the lifespan of the machinery, and maintenance costs.
Reasons You Need to Perform Regular Shaft Alignment
- Wear and Damage to Machine Components: Incorrect shaft alignment causes rapid wear and tear on machine components such as bearings, seals, and couplings due to unwanted friction and impact forces. This accelerated wear reduces the machine’s lifespan and increases the frequency of repairs.
- Increased Energy Consumption: A misaligned shaft causes the machine to consume more energy during operation due to increased resistance and friction. Higher energy consumption results in higher operating costs and decreased energy efficiency.
- Severe Damage and Production Interruptions: If the machine cannot continue to operate, it may lead to breakdown maintenance. Incorrect shaft alignment can cause severe damage, such as shaft breakage, bearing failure, or coupling damage. These issues can cause the machine to stop working and disrupt production, leading to financial losses and production downtime.
- Safety Risks: Machines with incorrect shaft alignment pose safety risks to employees. Vibration and unstable operation can lead to accidents and injuries. Proper shaft alignment reduces the risk of accidents and enhances workplace safety
- Wear and Damage to Machine Components: Incorrect shaft alignment causes rapid wear and tear on machine components such as bearings, seals, and couplings due to unwanted friction and impact forces. This accelerated wear reduces the machine’s lifespan and increases the frequency of repairs.
EP1. Basic of Shaft alignment
Shaft alignment is an essential and critical process for maintaining the balance and efficiency of machinery. Proper shaft alignment not only helps reduce wear and extend the lifespan of the machinery but also decreases energy consumption, prevents severe damage, reduces noise and vibration, enhances workplace safety, and improves production efficiency. Therefore, investing time and resources in correct shaft alignment is a worthwhile long-term investment.
EP 4 What is Offset and Angular
- Offset refers to an alignment error caused by the axes of two shafts (such as a drive shaft and a driven shaft) not being collinear in a parallel direction. This means there is a distance between the axes of the two shafts in a parallel direction, which can occur in either the horizontal or vertical direction. Measuring offset is crucial because alignment with offset causes increased friction and wear, as well as machine vibration.
- Angular refers to an alignment error caused by the axes of two shafts not being collinear in an angular direction. This means the axes of the two shafts are not parallel but have an angle between them, which can occur in either the horizontal or vertical plane. Measuring angular misalignment is important because alignment with angular errors causes uneven wear on machine components such as bearings or couplings, potentially leading to damage of these parts.
EP 9 Do not avoid Soft Foot Alignment
What is Soft Foot ?
Soft Foot refers to a condition where the base of the machine or shaft is uneven or imbalanced when mounted on the mounting base. This condition can prevent the machine from being properly aligned and impact its operational efficiency. Additionally, it can lead to other issues such as vibration, component wear, and unstable operation.
Causes of Soft Foot
- Uneven Base Surface: An uneven or inconsistent surface can cause the machine to shift when secured to the mounting base.
- Incorrect Installation: Improper machine installation or uneven tightening of bolts can lead to a soft foot condition.
- Distortion of the Base Structure: A weak or distorted base structure can prevent the machine from being securely installed.
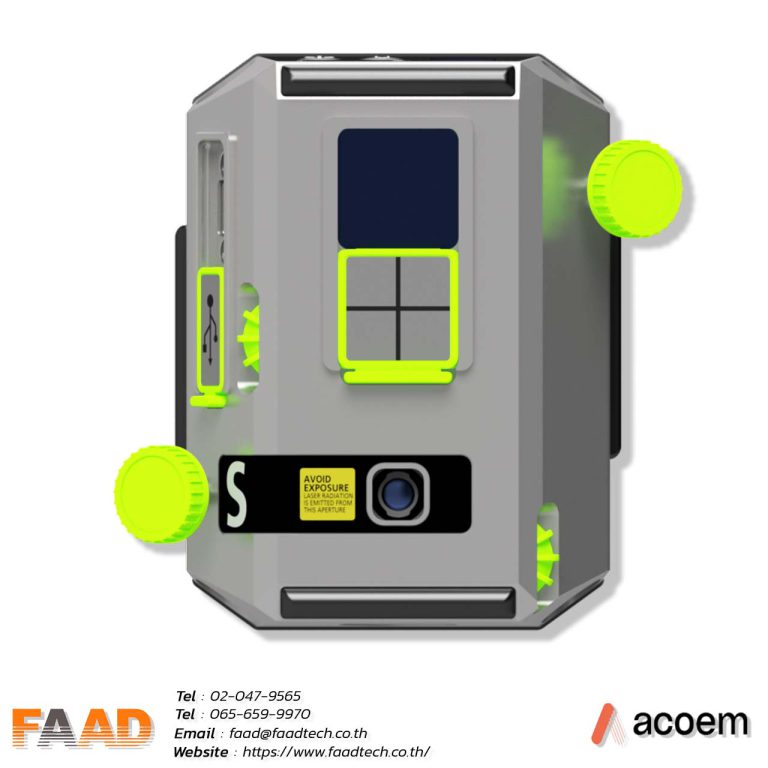
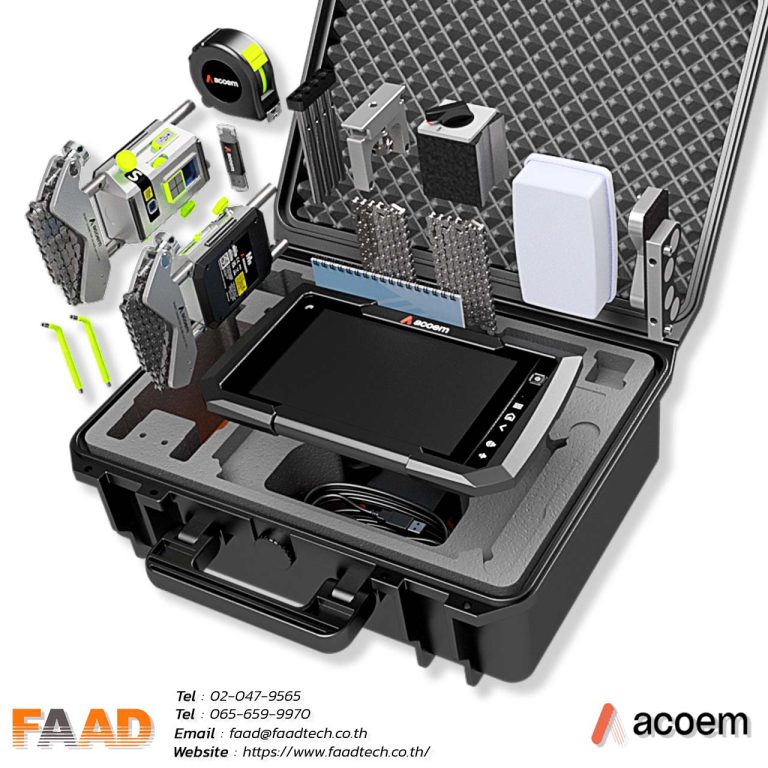
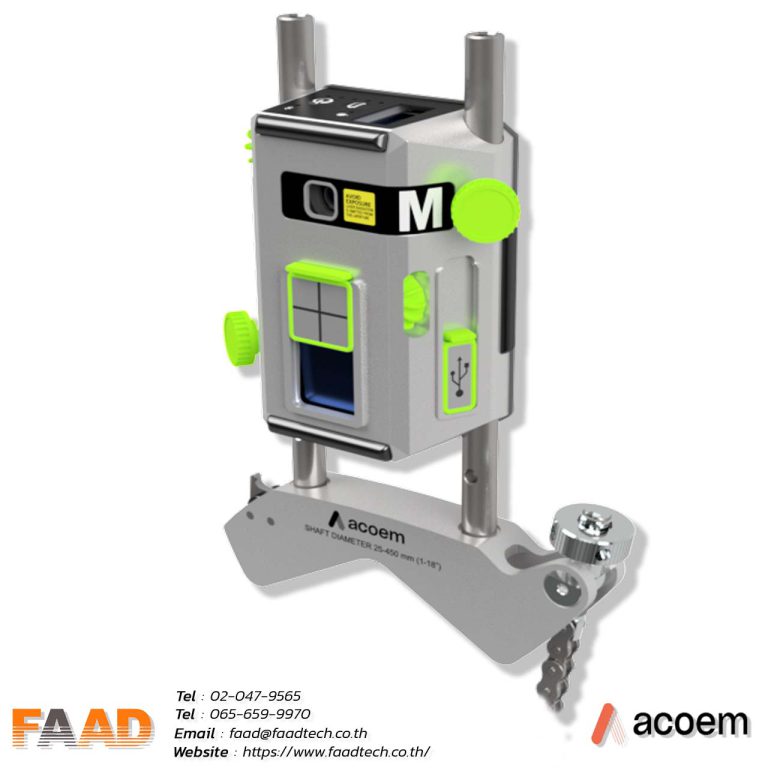



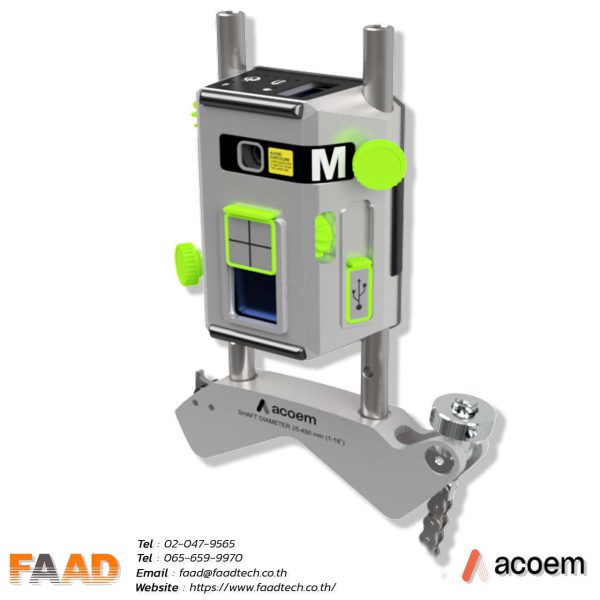
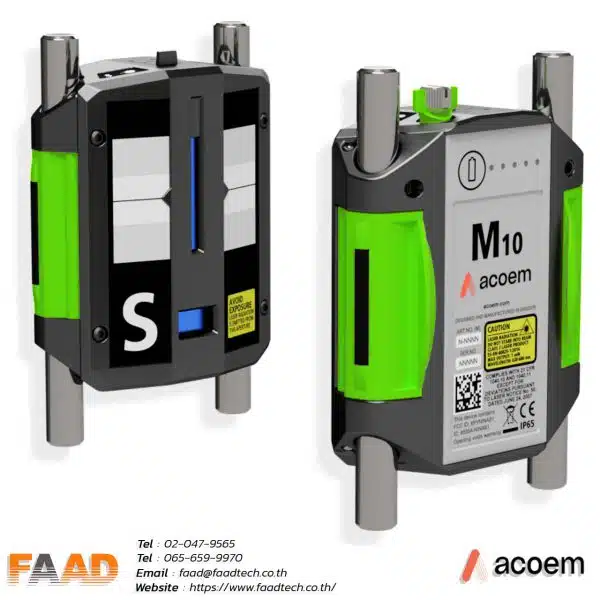
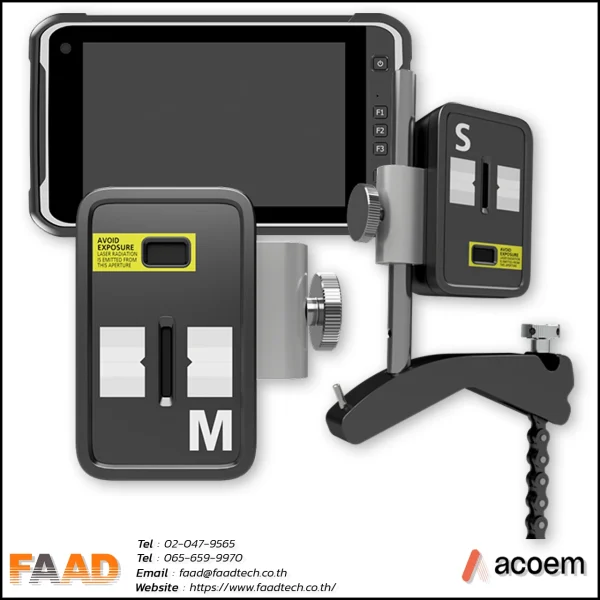
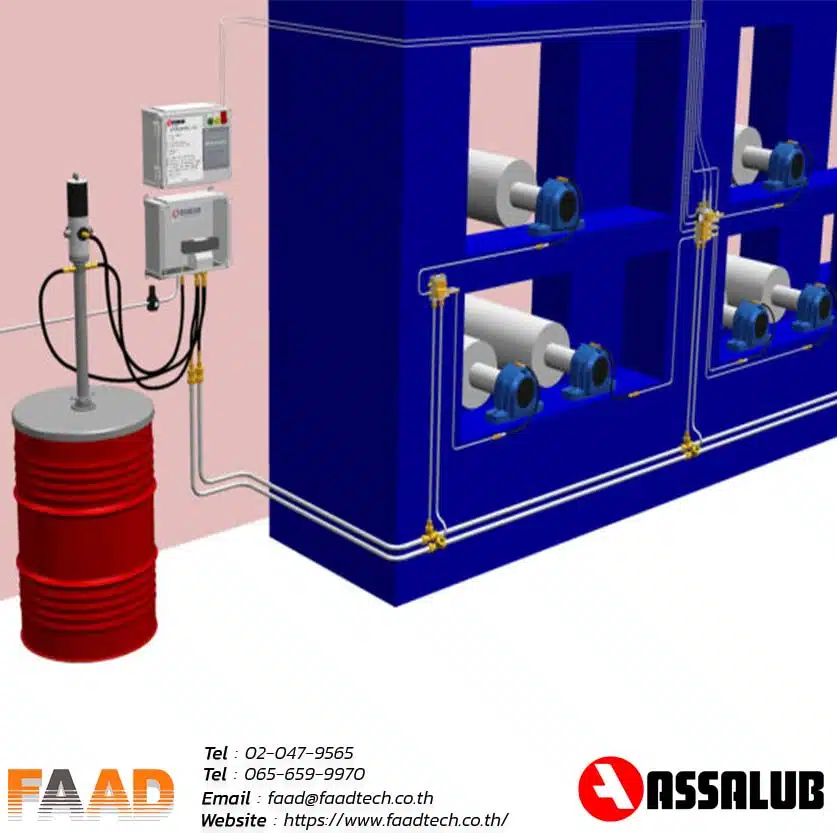
ACOEM : Laser shaft alignment AT400
Laser shaft alignment AT400
Maximize machinery performance with our 2-axis shaft alignment tool. Achieve precise alignment, minimize vibration, and extend equipment lifespan
- Unleash productivity and efficiency with advanced sensors and precise 2-axis measurement, delivering superior results across diverse applications.
- Intuitive and user-friendly interface for simplified navigation and an enhanced user experience.
- Introducing the market’s thinnest 2-axis sensor, weighing 306 g. With a 20-meter measurement range, it revolutionizes precision applications with its compact design and exceptional accuracy.
The large detector features a 20×20 mm2 size and offers a high-resolution of 0.001 mm, making it ideal for precise position sensing and different measurement applications.


Tripoint™ method
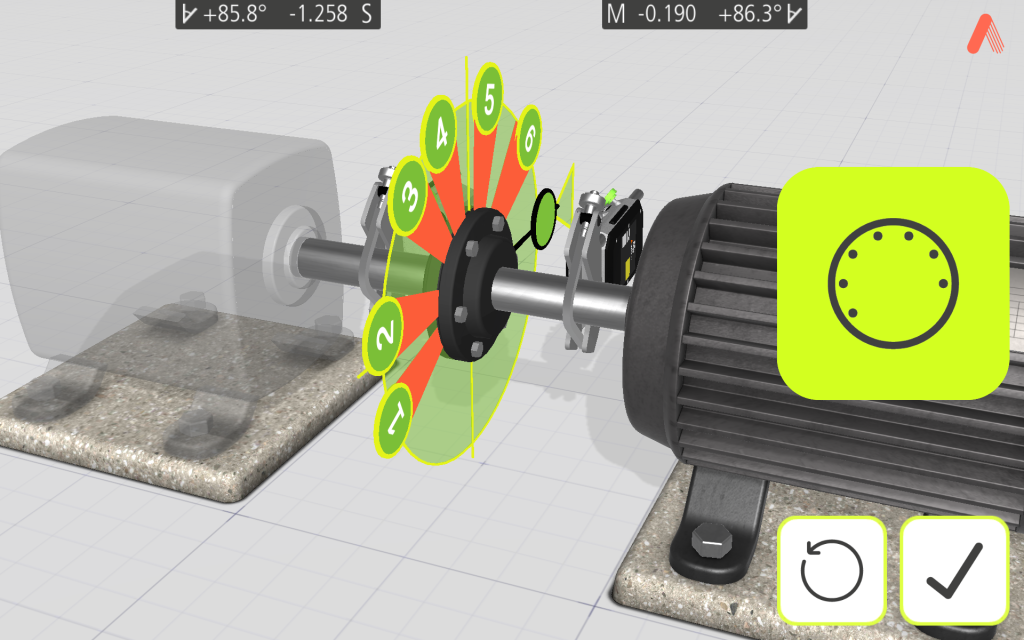
In the Tripoint method, the alignment condition can be calculated by taking three points while rotating the shaft at least 60°. In this method, all points are taken manually.

TRIPOINT Express™ method
This method seamlessly incorporates the Tripoint approach, offering the added advantage of fully automated measurements throughout the process.

Clock™ method
Clock™ In the Clock method, machinery positions are calculated by taking three points with 180° of rotation.

Multipoint method
This function enables measurement initiation from any position on the rotation, allowing recording of multiple points for optimized calculations. Ideal for turbine and sliding bearing applications.

Multipoint Express method
Our method follows the classic Multipoint method approach, but with the advantage of automated measurements for greater convenience.

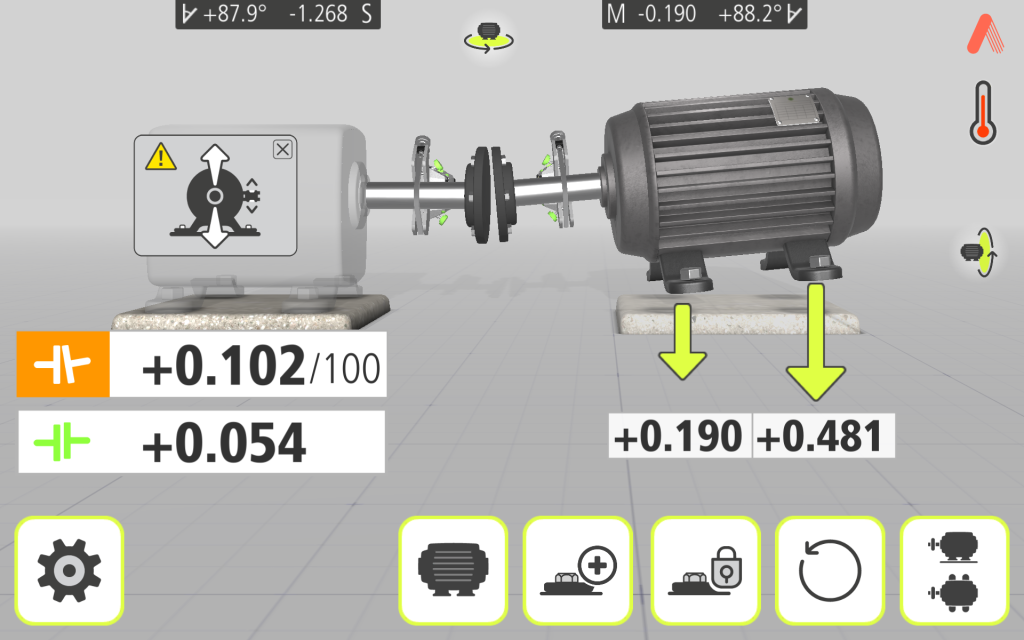
GuideU™,
Effortlessly navigate through our user-friendly interface, GuideU™, designed to make it a breeze to follow and understand.

True Live™
Get the position of both the shafts in real time with Acoem True Live™ feature

PDF EXPORT
Once the measurement is finished, you can generate a comprehensive PDF report that includes graphs and measurement data, providing detailed documentation of the measurement object.

Camera
Take pictures of your machines and setup to illustrate automatically in the report

Sync
Centralize and share your reports with your team, consolidate your plant’s alignment status, and assign alignment workorders to team members.
PRODUCT ALIGNMENT :













Read Our Latest News
News & Articles
- By Admin Faadtech
- Comments are off for this post.
- By Admin Faadtech
- Comments are off for this post.